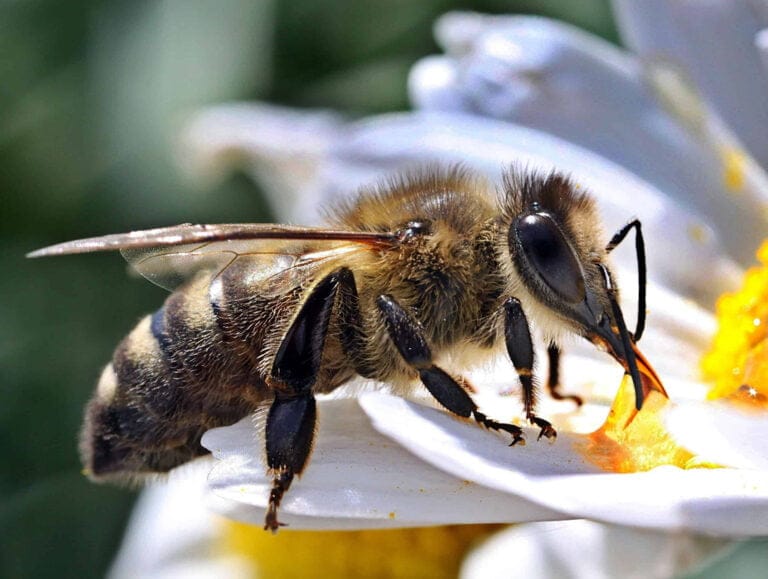
How to Identify the Dark European Honey Bee
The Dark European Honey Bee has a black or dark brown body with minimal banding. It thrives in gardens, forests, and meadows, where it plays a crucial role in pollination.
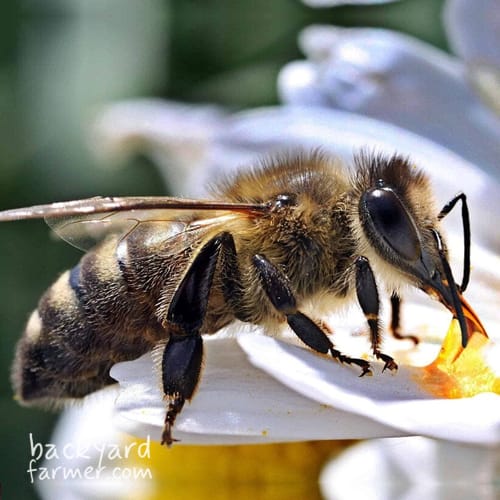

Physical Characteristics
- Queen – Largest in the colony, dark brown or black, robust build.
- Worker – Slightly smaller than the queen, black or brown, fine greyish hairs on the thorax.
- Male (Drone) – Larger eyes, more robust than workers, lacks a stinger.
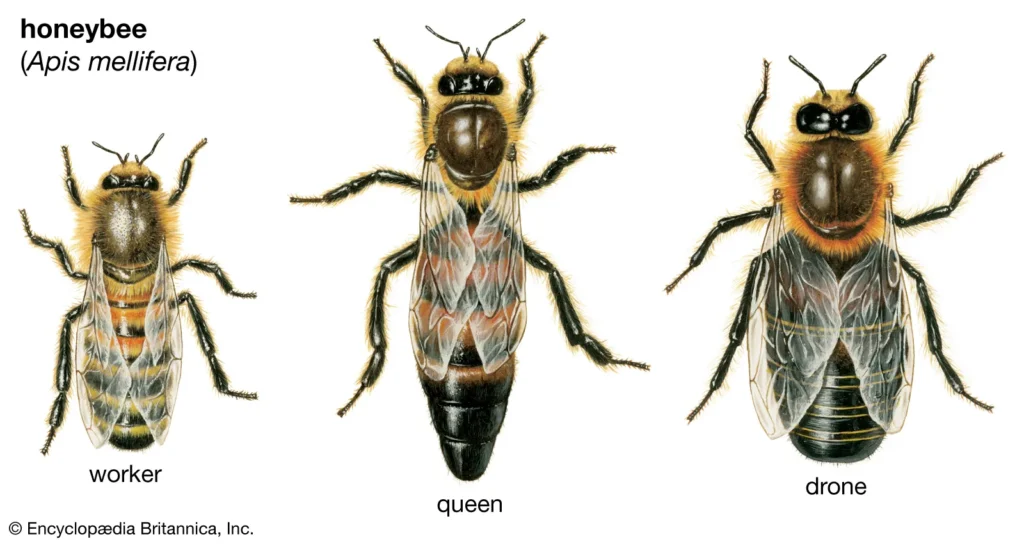
Image from Britannica.
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Common Name | Dark European Honey Bee |
| Latin Name | Apis mellifera mellifera |
| Size | 12-14 mm |
| Location | Native to Northern and Western Europe |
| Active Months | Year-round in warmer climates, April to October in temperate regions |
| Habitat | Gardens, forests, meadows, and agricultural areas |
| Nesting Behavior | Cavity nester (colonies in hollow trees or hives) |
| Social Behavior | Highly social, forming large colonies |
| Flora & Fauna | Pollinates fruit trees, wildflowers, and crops |
| UK Status | Threatened due to hybridization and habitat loss |



Similar Species
The Dark Apis mellifera mellifera is often mistaken for other bee species due to its dark coloration. Here’s how to differentiate it:
- Western Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) – Lighter golden-brown body with distinct yellow banding.
- Carniolan Honey Bee (Apis mellifera carnica) – Greyish-brown color, slightly smaller than the Dark European Honey Bee.
- Buckfast Bee – Hybrid species with a mix of brown and yellow tones, bred for gentleness.
Discover more about identifying UK bees in our comprehensive Bee Identification Guide.
Why Apis mellifera mellifera Matter
The Dark European Honey Bee is vital for pollination, helping maintain biodiversity and supporting food production. It sustains wildflowers and crops, making it an essential species. However, habitat loss and hybridization threaten its survival.
How You Can Help
Protecting the Dark European Honey Bee ensures a thriving ecosystem. Here’s how you can support them:
Plant Bee-Friendly Flowers
- Wildflowers, fruit trees, clover, and lavender.
Avoid Harmful Pesticides
- Neonicotinoids, glyphosate, and synthetic insecticides.
Provide Nesting Spaces
- Install bee-friendly hives, protect hollow trees, and maintain diverse natural spaces.
Encouraging pollinator-friendly gardening ensures that the Apis mellifera mellifera Honey Bee and other beneficial species continue to thrive. Explore these WWF tips on creating a bee-friendly garden to support pollinators.







