Short answer: Yes — LED grow lights absolutely work when matched to your plants’ needs. This guide explains how they work, why they’re effective, and how to use them correctly for healthy, high‑yield indoor gardens.
Myth vs Fact: What People Get Wrong About LED Grow Lights
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| “LEDs are too weak for real yields.” | Modern LEDs now match or beat HPS in both yield and quality, while using up to 50 % less energy. |
| “Blurple lights are the best.” | Early LEDs used narrow red/blue bands, but full‑spectrum white with red boosters now produces stronger growth and better visibility. |
| “More watts means better growth.” | Efficiency (µmol/J) and PPFD uniformity matter more than raw wattage. |
| “You need expensive UV bars to get potency.” | UV can help slightly, but genetics and environment have a far greater impact. |
Do LED Grow Lights Really Work?
If you’ve spent any time on grow forums, Reddit threads, or YouTube grow channels, you’ve probably seen this question pop up again and again: Do LED grow lights really work?
It’s a fair question — especially if you remember those early “blurple” LED panels that promised huge yields but barely kept seedlings alive.
Thankfully, things have changed. Modern LED grow lights are brighter, more energy-efficient, and engineered to deliver exactly what plants need. They produce full-spectrum light that mimics natural sunlight, generate strong PPFD levels, and cost far less to run than older HID or fluorescent systems.
What This LED Grow Light Guide Covers
This guide explains the LED grow light basics — how they work, why full-spectrum lighting matters, and what essential terms like PAR, PPFD, and efficacy (µmol/J) mean in practical growing terms.
Whether you’re cultivating cannabis, herbs, or leafy greens, we’ll cut through marketing noise and focus on what actually produces results. You’ll learn how light spectrum, distance, and duration affect plant growth — backed by both grower experience and scientific research.
What You’ll Learn in This Article
- How LED grow lights create plant-usable light and why the light spectrum is key to healthy, vigorous growth.
- What PPFD and DLI mean, and how to measure light intensity accurately at each growth stage.
- How to optimise fixture height, distance, and dimmer settings for better yield and efficiency.
- What experienced indoor growers have discovered about balancing cost, power, and performance for consistent results.
By the end of this guide, you’ll know not just why LED grow lights work, but how to make them work for you. From choosing the right light spectrum and wattage to setting up an energy-efficient indoor grow light system, you’ll have everything you need to start growing smarter — and greener.
Continue your LED grow light & indoor gardening knowledge
- Maximizing plant growth with LED grow lights – Learn how to set up and run your lights efficiently for vigorous growth across different plant types
- How to choose the right LED grow lights for your indoor garden – A complete guide to selecting the ideal spectrum, power, and features for your growing goals
- Budget-friendly LED grow lights for indoor gardening – Options and tips for growers who want good performance without overspending
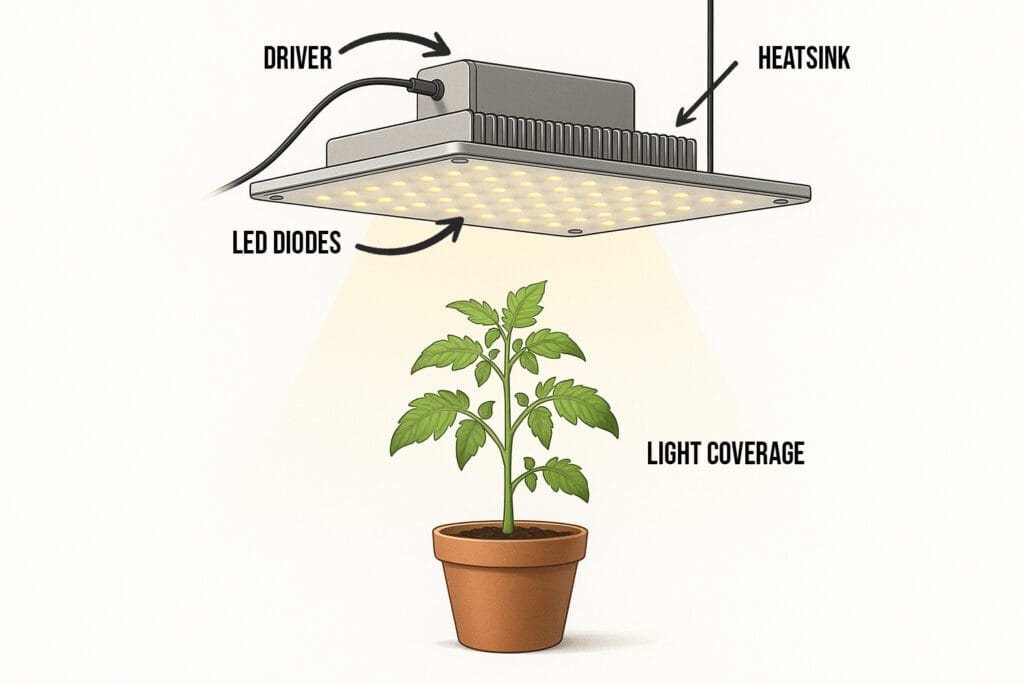
How LED Grow Lights Work (The Basics)
Modern LED grow lights convert electricity into plant-usable light within the photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) range of 400–700 nanometres (nm). This light range is crucial for photosynthesis — it’s where plants absorb energy to produce chlorophyll, strengthen stems, and grow healthy leaves.
Unlike older HPS (High-Pressure Sodium) or fluorescent grow lights, which waste much of their energy as heat, LED grow lights are built for efficiency. They emit specific wavelengths with a high photon output, providing more PAR light per watt and less wasted energy. This results in cooler temperatures, lower electricity costs, and a safer growing environment — ideal for both cannabis and vegetable growers.
How LED Grow Lights Produce Plant-Usable Light
Each LED diode emits light at a specific wavelength. By combining blue (around 450 nm), red (around 660 nm), and broad-spectrum white diodes, manufacturers can closely mimic natural sunlight and create the perfect balance for indoor plant growth.
Key benefits of LED grow light technology:
- Precision: Fine-tune the light spectrum to match each growth stage.
- Efficiency: Modern LED chips reach 2.5–3.0 µmol/J, converting nearly every watt into usable PAR light.
- Longevity: Quality LED grow lights last 50,000+ hours, delivering consistent, high-quality light output for years.
Why LED Grow Lights Outperform Traditional Systems
Traditional systems like HPS or metal halide (MH) lamps produce excess heat and use more power. LEDs solve this problem by providing focused, cool-running light that plants can absorb more effectively.
| Feature | LED Grow Light | HPS / MH Light |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | 2.5–3.0 µmol/J | 1.2–1.7 µmol/J |
| Heat Output | Low | High |
| Lifespan | 50,000+ hours | 10,000–20,000 hours |
| Spectrum Control | Tunable / Full-spectrum | Fixed |
| Power Use | 30–50% less | Higher running cost |
The bottom line: Quality LED grow lights easily outperform traditional systems in both yield and quality. When spectrum, PPFD, and timing are adjusted correctly, you’ll achieve faster growth, stronger plants, and higher-quality harvests.
Common Misconceptions About LED Grow Lights
“LEDs can’t handle full harvests.” — False. Modern full-spectrum LEDs provide the PPFD levels required for flowering and fruiting.
“Any LED will work for growing plants.” — Incorrect. Regular household bulbs don’t offer the right PAR spectrum or intensity.
“LEDs produce no heat.” — Misleading. While they run cooler than HPS systems, the diodes and driver still generate some warmth.
Key Takeaway: Modern LED grow light systems work because they deliver exactly what plants need — the right light spectrum, PPFD, and efficiency — without wasting energy as heat. When you manage distance, schedule, and setup correctly, you’ll see vigorous growth and high yields, whether you’re nurturing herbs, salad greens, or flowering cannabis plants indoors.
Why Spectrum Matters
The light spectrum your grow light produces — the full range of wavelengths from blue to red — directly influences how your plants grow, develop, and yield. Each colour triggers different plant responses, from strong vegetative growth to dense, resinous flowers. Understanding how the LED grow light spectrum works lets you fine-tune your setup for healthier, more productive plants.
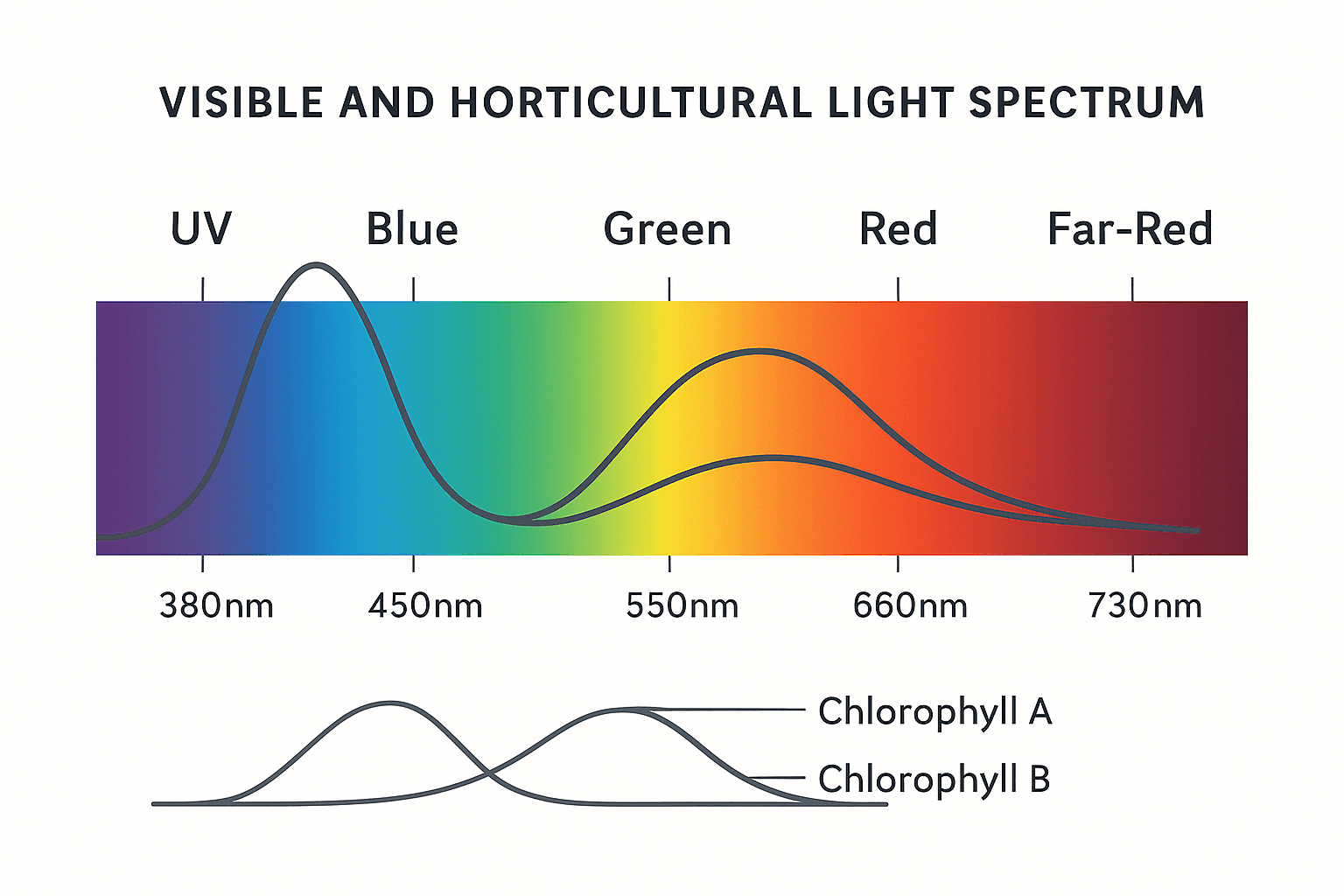
Plant growth peaks in red (around 660 nm) and blue (around 450 nm) light, with far-red aiding flowering stretch.
The Role of Different Wavelengths in Plant Growth
Plants use light within the photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) range of 400–700 nanometres (nm). Each wavelength has a specific role in shaping plant structure, leaf size, and flowering behaviour.
| Light Band | Wavelength (nm) | Plant Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Blue Light | 430–470 nm | Encourages compact growth, tight node spacing, and strong stems — essential during the vegetative stage. |
| Green Light | 500–570 nm | Penetrates deeper into the canopy, helping shaded leaves photosynthesise and improving uniform growth. |
| Red Light | 620–670 nm | Boosts photosynthesis, promotes root development, and triggers flowering and fruiting. |
| Far-Red Light | 700–750 nm | Affects stretch and bloom timing — when used strategically, it can help speed up flowering. |
| UV (Ultraviolet) | 280–400 nm | In small amounts, enhances resin and oil production, colour, and flavour — but too much causes stress. |
Tip: Balanced lighting across the full PAR spectrum produces steady, uniform growth while avoiding plant stress.
Full-Spectrum LED Grow Lights: Mimicking Natural Sunlight
A full-spectrum LED grow light combines all these wavelengths into a balanced output that closely matches real sunlight. This broad range supports plants from seedling through harvest without the need to swap bulbs or fixtures.
Key benefits of full-spectrum LED grow lights:
- Consistent growth across all plant stages.
- Less stress when switching from veg (18/6) to flower (12/12) cycles.
- Even canopy development with improved light coverage.
- Natural white light that’s easier on the eyes when tending plants.
For most home growers, a white + red spectrum blend offers the ideal balance of efficiency, light penetration, and overall plant performance.
Narrow-Band vs Full-Spectrum LEDs
Early LED grow lights used red and blue diodes, producing that familiar purple “blurple” glow. While these early lights supported photosynthesis, plants grown under narrow-band LEDs often showed weak stems, thin foliage, and inconsistent growth.
Modern white-based full-spectrum LEDs fix these issues by covering the entire PAR range. The difference is clear:
- Stronger, more natural plant structure.
- Improved nutrient uptake and pigment development.
- Richer flavours, aromas, and resin production in flowering plants.
Real-World Grower Experience
Experienced indoor growers often experiment by adding small amounts of far-red or UV light during late vegetative or flowering stages. This can enhance colour, improve flowering speed, and boost terpene production. However, moderation is key — too much far-red leads to stretching, while excessive UV can damage leaves.
If you’re choosing between different LED spectrums for specific crops, my guide on the best LED grow lights for different types of plants breaks down what works best for leafy greens, herbs, and fruiting plants.
Grower Tip: Think of far-red and UV as seasoning. A little adds depth and strength — too much spoils the recipe.
Summary: Understanding your LED grow light spectrum is the foundation of efficient indoor gardening. When your light output matches your plants’ natural requirements, you’ll achieve faster growth, stronger stems, and higher yields — all while saving energy and avoiding the heat issues common with older grow light systems.
Understanding PAR, PPF & PPFD
When talking about LED grow lights and indoor lighting systems, growers often mention PAR, PPF, and PPFD. These aren’t just technical buzzwords — they’re essential for understanding how much usable light your plants actually receive and how efficiently your LED grow light performs.
What Is PAR in LED Grow Lights?
PAR (Photosynthetically Active Radiation) represents the light wavelengths plants use for photosynthesis — between 400–700 nanometres (nm). While it’s not a measurement by itself, PAR defines the spectrum of light that fuels plant growth.
If your LED grow light spectrum doesn’t emit strong output in this range, part of that energy is wasted as unusable light. Choosing a full-spectrum fixture ensures your plants get the most from every watt of power.
For a deeper look at the science behind LED spectrum and plant response, see Fluence’s horticultural lighting research.
What Is PPF?
PPF (Photosynthetic Photon Flux) measures how much light your fixture produces within the PAR range each second. It’s expressed in micromoles per second (µmol/s).
Think of PPF as your grow light’s horsepower — the total number of light photons emitted every second. A higher PPF rating means greater light potential for growth, but it doesn’t yet tell you how much of that light reaches your plants.
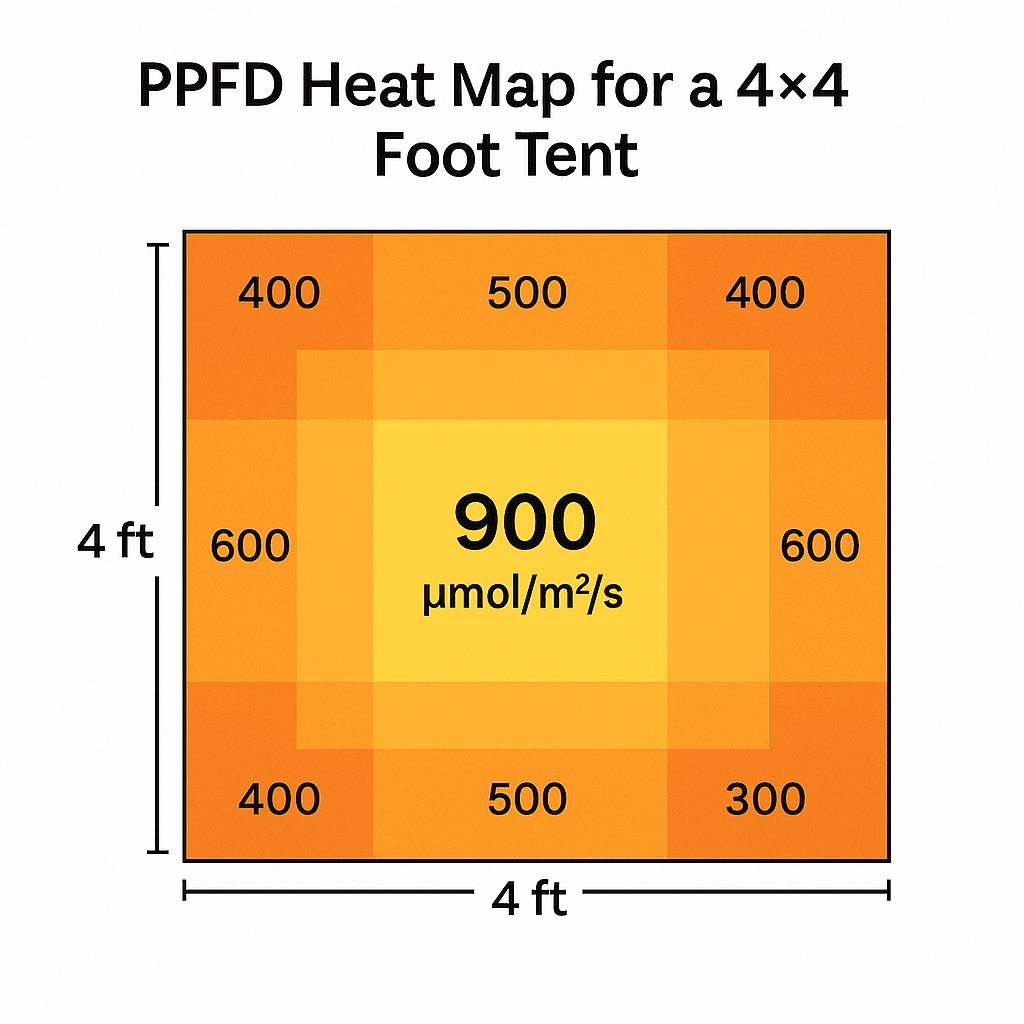
What Is PPFD?
PPFD (Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density) measures how much of that usable light actually hits the plant canopy. It’s recorded in micromoles per square metre per second (µmol/m²/s).
While PPF measures output, PPFD measures delivery — and that’s the one that truly matters. It shows how efficiently your plants absorb the light energy you’re paying for. Monitoring PPFD is the best way to ensure your LED grow light setup is working as effectively as possible.
Ideal PPFD Levels for Each Growth Stage
| Growth Stage | Target PPFD (µmol/m²/s) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Seedlings | 100–200 | Gentle, low-intensity light helps prevent stretching. |
| Vegetative | 400–600 | Encourages fast, healthy leaf and stem development. |
| Flowering / Fruiting | 700–900 | Boosts density, colour, and yield quality. |
Tip: Going above 1,000 µmol/m²/s without added CO₂ can cause light stress. Always increase intensity gradually.
How to Measure PPFD Accurately
The best way to measure light intensity is with a quantum sensor or PAR meter (like the Apogee MQ‑500). For a more budget-friendly option, the Photone app can deliver decent results when calibrated correctly.
For accurate readings:
- Measure multiple points — centre, corners, and edges of the canopy.
- Aim for a uniformity ratio of 0.7 or better for even growth.
- Improve reflectivity with Mylar sheets or matte white walls, boosting PPFD by up to 20%.
Watts vs PPFD: A Common Misconception
Many growers still rely on watts per square foot to measure lighting strength, but wattage only indicates power draw — not efficiency or usable light. A 300-watt LED grow light can outperform a 600-watt HPS fixture if its diodes and optics are more efficient.
That’s why focusing on PPFD measurements gives a much clearer picture of your grow light’s real performance.
For a deeper look at real-world tent setups and PPFD coverage, check out my in-depth review of the best LED grow lights for a 4×4 tent (UK). It includes tested measurements, ideal hanging heights, and practical setup tips.
Summary:
Understanding PAR, PPF, and PPFD helps you fine-tune your LED grow light system for the best results. Prioritise PPFD readings over wattage to measure what really matters: how much light your plants actually receive. With the right combination of intensity, distance, and coverage, you’ll achieve stronger growth, higher yields, and more efficient energy use — all while keeping your setup cool and cost-effective.
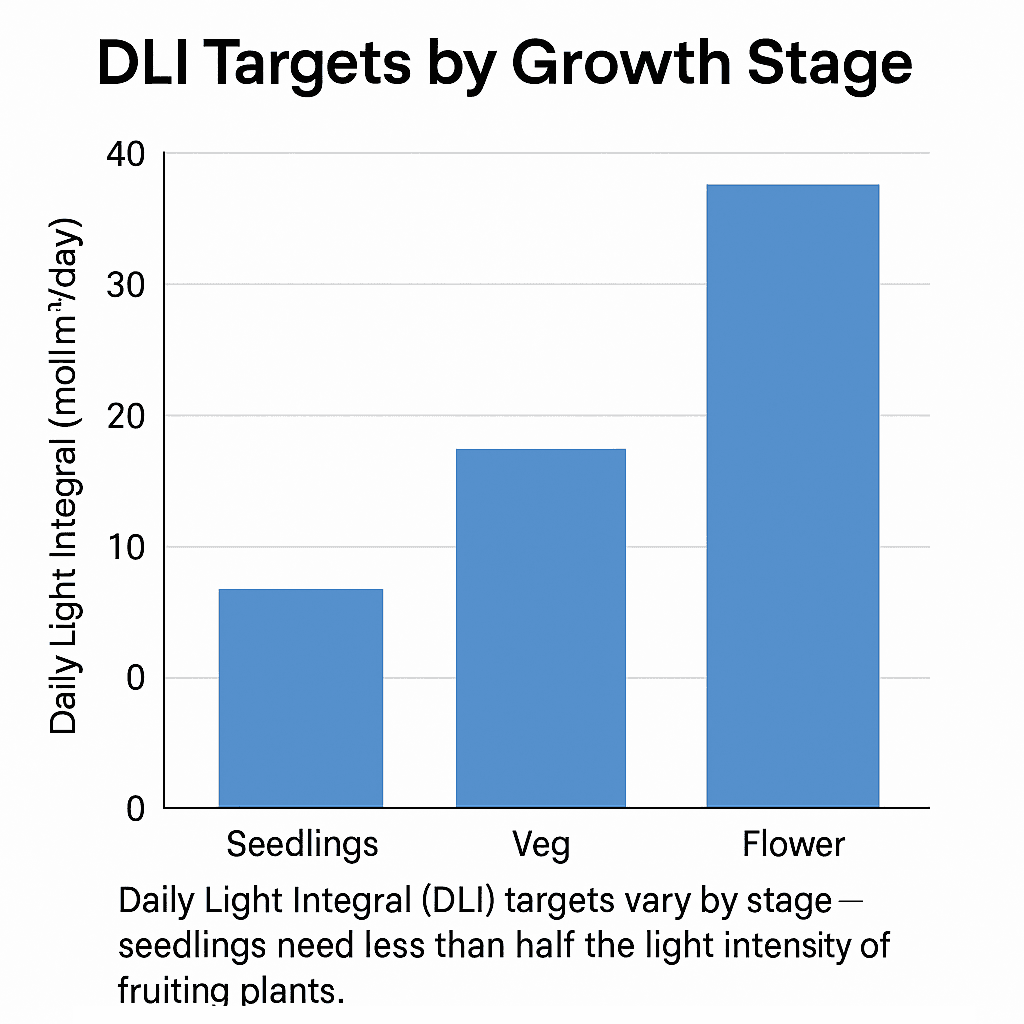
Light Intensity, Distance & Growth Stages
Getting LED grow light intensity right at every stage of your plant’s life is one of the most important — and most misunderstood — parts of indoor growing. Too little light and your plants stretch weakly toward the source. Too much light and you’ll see bleaching, stress, or even lasting damage. The secret is finding the right balance by understanding Daily Light Integral (DLI), adjusting your LED grow light height, and reading your plants’ signals.
Understanding Light Intensity and DLI in LED Grow Lights
Light intensity changes naturally as plants develop through different growth stages. DLI (Daily Light Integral) measures how much total usable light (in mol/m²/day) your plants receive over a 24-hour period. It combines both light intensity (PPFD) and photoperiod (light duration).
| Growth Stage | Target PPFD (µmol/m²/s) | Hours of Light | Approx. DLI (mol/m²/day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling | 150 | 18 | 10 |
| Vegetative | 400 | 18 | 26 |
| Flowering / Fruiting | 800 | 12 | 35 |
Tip: If your LED grow light isn’t especially powerful, extend your light hours to reach your DLI target. This is an easy way to maintain healthy growth in smaller grow tents or low-watt setups.
Adjusting LED Grow Light Height by Growth Stage
As your plants mature, the correct LED grow light distance changes too. Getting this wrong is one of the quickest ways to stunt growth or cause light burn.
| Growth Stage | Recommended Height | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Seedlings | 60–75 cm | Keep lights high or dimmed to protect delicate new growth. |
| Vegetative | 45–60 cm | Strong, even light encourages structure and root development. |
| Flowering / Fruiting | 30–45 cm | Bring lights closer to increase density, colour, and yield. |
Key Guidelines for LED Light Height
- Start with lights high above the canopy and lower them gradually as plants adapt.
- Watch for leaf tacoing or bleaching — both are early warning signs of excess light intensity.
- Maintain steady airflow between the canopy and fixture to prevent heat buildup.
Balancing Multiple LED Grow Lights
If you’re using a larger grow tent, two medium-sized fixtures often outperform one large unit. You’ll achieve better light coverage, more consistent PPFD, and fewer hotspots.
Pro Tip: For uneven canopies, try angling or offsetting your lights slightly. This diagonal setup improves side light penetration and keeps growth uniform across all plants — tall or short.
Common LED Grow Light Mistakes
- Turning up intensity too soon after transplant — shocks young plants and causes leaf curl.
- Ignoring tent edges — outer plants often stretch toward the central light source.
- Overlooking canopy heat — even efficient LEDs can raise leaf temperatures above 28°C.
Summary
Getting LED grow light intensity right isn’t about blasting your plants with as much light as possible — it’s about maintaining balance. Measure PPFD at canopy level, adjust your LED grow light height regularly, and observe your plants closely. With small, steady adjustments, you’ll find that sweet spot where light, heat, and growth align perfectly for maximum yield and efficiency.
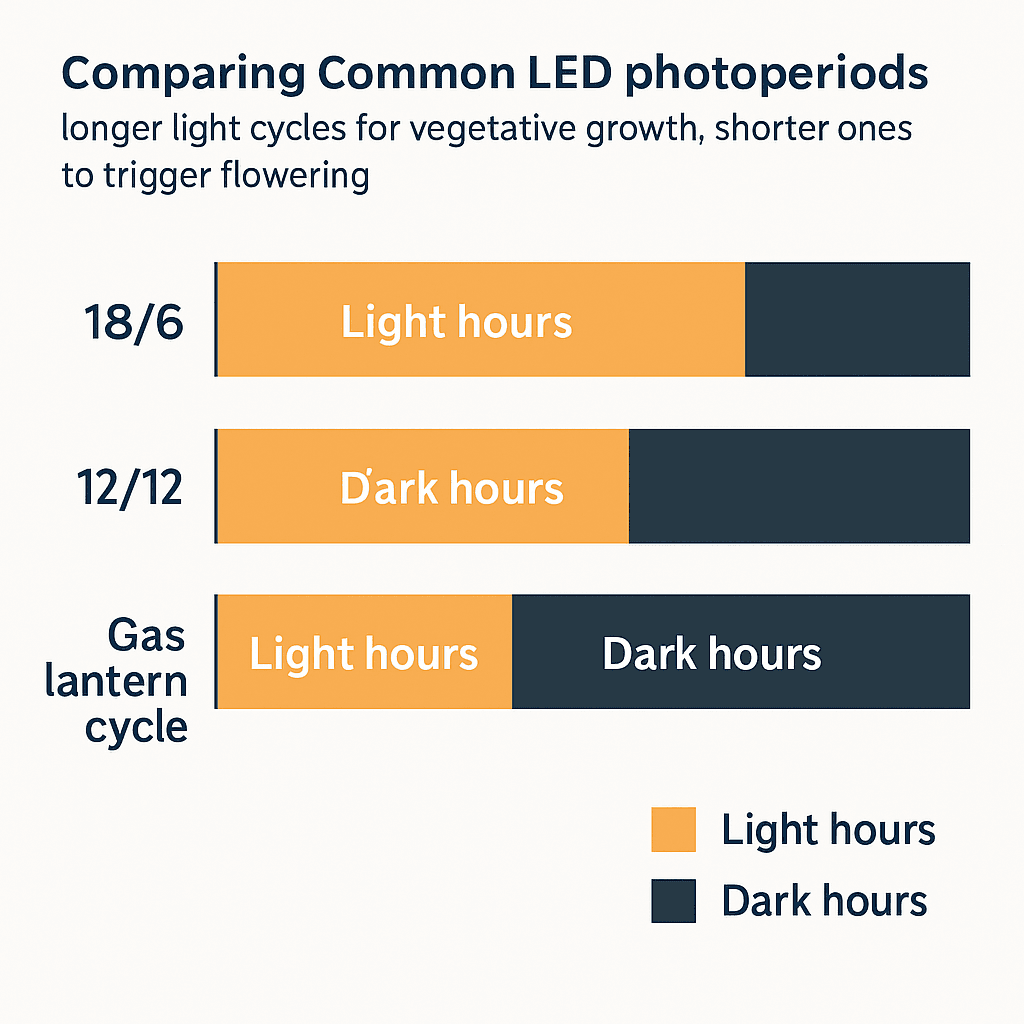
Daily Light Hours & Photoperiods
The number of light hours your plants receive each day — known as the photoperiod — is just as important as LED grow light intensity. It doesn’t just influence how fast your plants grow but also determines when they begin to flower or fruit. Since different species — and even varieties within the same species — respond differently to day length, understanding this helps you time growth for consistent, healthy yields.
How Photoperiods Affect Plant Growth
Plants use light duration as a signal to decide when to remain in vegetative growth or transition into flowering. Longer days promote steady, leafy growth, while shorter days often trigger flowering and fruiting. Getting the photoperiod lighting schedule right ensures your plants stay balanced, efficient, and productive.
| Plant Type | Common Light Schedule | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetables & Herbs | 16–18 hours light / 6–8 hours dark | Encourages consistent vegetative growth for greens, herbs, and seedlings. |
| Photoperiod Cannabis / Flowering Plants | 18/6 (veg) → 12/12 (flower) | Mimics the natural transition from summer to autumn. |
| Autoflower Cannabis | 18/6 or 20/4 | Flowers automatically, regardless of day length. |
| Leafy Greens (Lettuce, Spinach) | 14–16 hours | Prevents premature bolting while supporting healthy leaf growth. |
Non-Traditional LED Light Cycles
Some experienced growers experiment with alternative light schedules to reduce energy use or manage heat, though these methods require careful monitoring and patience.
6/2 Cycle
This method runs six hours on and two hours off, repeated three times daily for a total of 18 light hours. It helps manage heat buildup and gives plants short recovery periods throughout the day.
Gas Lantern Routine (GLR)
The Gas Lantern Routine uses 12 hours of light, 5.5 hours of darkness, one hour of light, then another 5.5 hours of darkness. That single “interrupt” hour keeps plants in the vegetative stage while cutting power costs.
While both methods can work well for some growers, they require experimentation. For most home setups, sticking to the classic 18/6 or 12/12 LED grow light schedule remains the most consistent and reliable choice.
You can also explore the best LED grow lights for indoor gardens if you’re growing on a smaller scale or looking for options with built-in dimmers and adjustable output for each stage.
Why Night Conditions Matter in Indoor Growing
The dark cycle isn’t wasted time — it’s when plants focus on root development, nutrient uptake, and hormone balance. Getting nighttime conditions right makes a noticeable difference in plant health, resilience, and yield.
Ideal Night Conditions for LED Grow Rooms:
- Keep temperature within 5–8°C of daytime levels to reduce stress and shock.
- Maintain humidity around 50–55% during late flower to prevent mould.
- Ensure gentle airflow to avoid condensation and keep foliage dry.
Advanced Tips for Photoperiod Control
Once you understand light timing, these advanced tips for using LED grow lights will help you fine-tune dimmers, timers, and photoperiod transitions for smoother growth and better efficiency.
Summary
A consistent photoperiod lighting schedule makes your grow space more predictable and energy-efficient. Longer light hours suit herbs and vegetables, while shorter cycles trigger flowering in cannabis and other bloom-heavy crops. Choose a lighting plan that suits both your plant type and your energy budget, and you’ll achieve healthier growth, smoother transitions between stages, and more reliable yields from your LED grow light setup.
Efficiency, Cost & Real-World ROI
LED grow lights are well known for being energy-efficient, but what does that actually mean for real-world growers? The goal isn’t just to buy the most powerful light — it’s to find the right balance between output, running costs, and long-term value. Once you understand these efficiency metrics, you can choose grow lights that deliver strong, healthy growth without inflating your electricity bill.
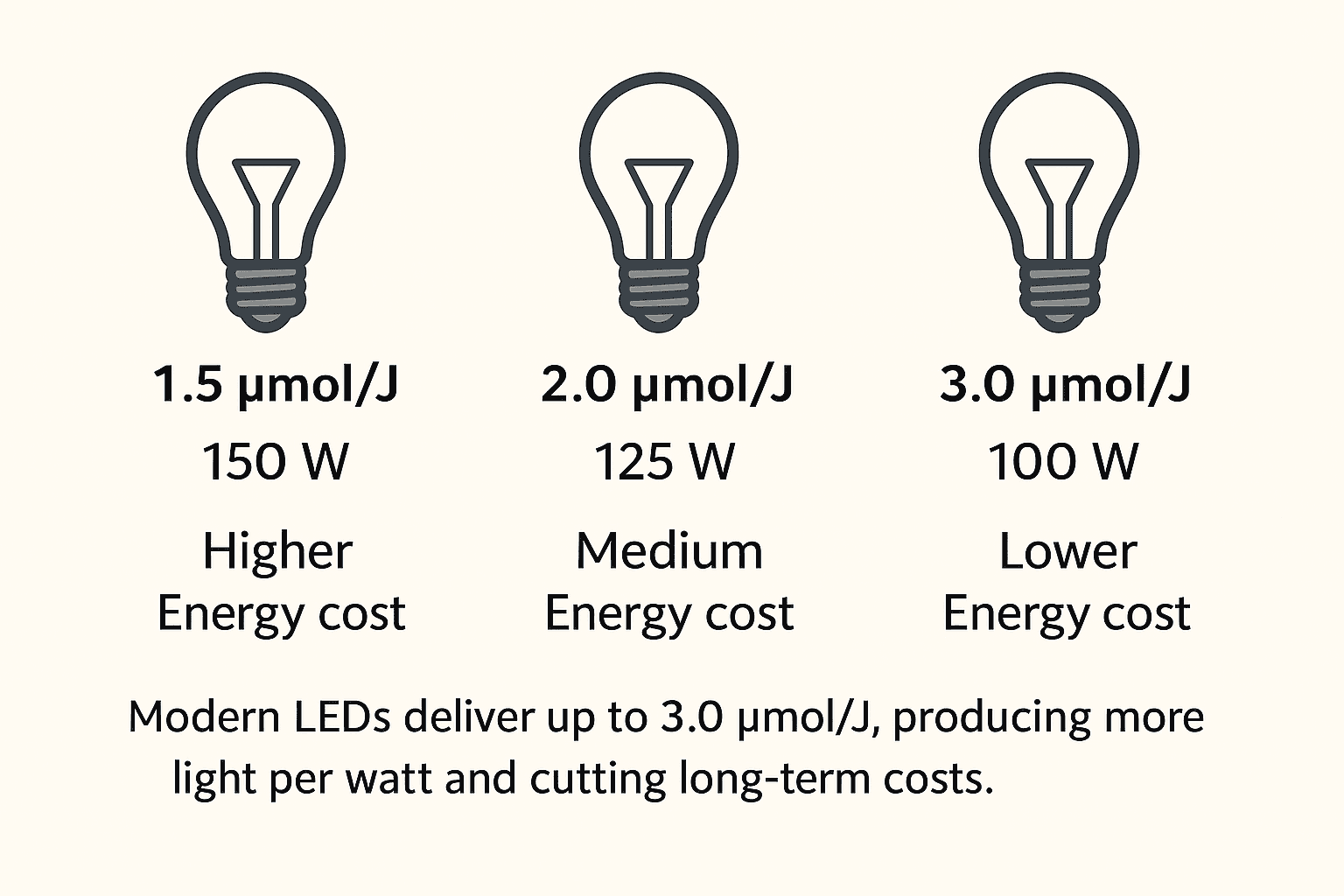
Understanding LED Grow Light Efficiency Metrics
The main measure of efficiency is µmol/J (micromoles per joule) — this indicates how much usable PAR light (photosynthetically active radiation) your fixture produces per joule of electricity consumed.
| Metric | Description | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Efficacy (µmol/J) | Light photons produced per watt of energy used | 2.5–3.5 µmol/J (modern LEDs) |
| Power Draw (Watts) | Actual energy use, not the “equivalent wattage” often advertised | 100–650 W (home to pro models) |
| PAR Output (PPF) | Total photosynthetic light output | 250–1700 µmol/s |
A higher µmol/J means your LED grow light converts electricity into usable light more efficiently. Premium full-spectrum LEDs now reach 3.0 µmol/J or higher — nearly twice the efficiency of older HPS lamps.
The Real Cost of Running LED Grow Lights
While LED grow lights are more efficient than HID or fluorescent systems, your running costs depend on wattage, light duration, and your electricity rate.
Quick LED Cost Example
Daily kWh = (Watts ÷ 1000) × Hours on
Daily Cost (£) = Daily kWh × Electricity Rate
If you run a 240W LED grow light for 18 hours per day:
- Total = 4.32 kWh/day
- At £0.30/kWh, that’s about £1.30/day or £40/month
Pro Tip: Using dimmers, timers, or off-peak hours can reduce costs by 20–30% without compromising growth.
Real-World Efficiency: What Growers Track
Many indoor growers prefer to measure efficiency using grams per watt (g/W) or grams per kilowatt-hour (g/kWh). These reflect how effectively your grow converts light and power into actual yield.
| Metric | Good Target | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| g/W | 1.0–1.5 | Achievable in balanced setups using full-spectrum LEDs |
| g/kWh | 1.3–2.0 | Measures yield per energy cost over time |
Performance varies by strain, environment, and experience, but these metrics help compare real-world light efficiency fairly.
To see how different models perform in terms of energy efficiency and yield, the Mars Hydro TSW 2000 review compares real-world power draw with harvest results — a great reference for anyone tracking grams per watt.
Maximising LED Efficiency at Home
- Add reflective surfaces: Mylar or flat white paint can boost light efficiency by up to 20%.
- Dim smartly: Reduce output during early growth to save power and prevent light stress.
- Run lights at night: Take advantage of cooler conditions and off-peak electricity rates.
- Maintain airflow: Keeps diodes cool and extends fixture lifespan.
- Clean fixtures regularly: Dust buildup can block 10% or more of total light output.
Common LED Grow Light Efficiency Myths
- “More watts mean more yield.” → False. Excess power often causes light stress and wasted energy.
- “Dimming cuts energy use completely.” → Partly true. It reduces energy draw but doesn’t eliminate it.
- “µmol/J is everything.” → Not quite. Coverage, diode quality, and optical design play just as big a role in real-world performance.
Summary
Efficiency isn’t just about high numbers — it’s about how well that light energy reaches your plants. By focusing on µmol/J, PAR output, and overall energy management, you’ll maximise growth, lower running costs, and get more yield from every watt of power. In short: grow smarter, not harder.
Quick Visual Guides
When setting up your LED grow lights, it helps to have all the key figures and measurements in one place. These quick visual guides simplify everything from PPFD targets to hanging height, energy cost, and DLI (Daily Light Integral) — ideal for both beginner and experienced indoor growers. Use them as a handy reference when adjusting your grow tent or fine-tuning light efficiency.
PPFD Targets by Growth Stage
| Growth Stage | Target PPFD (µmol/m²/s) | Recommended Light Height | DLI (mol/m²/day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling | 100–200 | 60–75 cm | 10 |
| Vegetative | 400–600 | 45–60 cm | 26 |
| Flowering / Fruiting | 700–900 | 30–45 cm | 35 |
Tip: Use a reliable PPFD meter or a calibrated app like Photone to measure your light levels accurately. Edge plants often receive 15–25% less light, so adjust your fixture height or angle to maintain even PPFD across the canopy.
Hanging Height Guide for LED Grow Lights
The correct LED grow light hanging height ensures your plants receive optimal intensity without heat stress or bleaching.
| Fixture Power | Recommended Hanging Height |
|---|---|
| 100–150 W | 60–75 cm |
| 200–300 W | 45–60 cm |
| 400–600 W | 30–45 cm |
Pro Tip: Recheck your hanging height weekly as your plants grow. Maintaining consistent PPFD readings at canopy level prevents stretching and encourages compact, even growth.
LED Grow Light Cost Estimator
Use this quick reference to estimate your energy use and running costs for different LED grow light setups.
| Fixture Power | Hours / Day | kWh / Day | Approx. Monthly Cost (£0.30/kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 150 W | 18 | 2.7 | £24.30 |
| 250 W | 18 | 4.5 | £40.50 |
| 400 W | 12 | 4.8 | £43.20 |
| 600 W | 12 | 7.2 | £64.80 |
Energy-Saving Tip: Use dimmers, timers, or staggered light cycles during early growth to reduce your LED power draw by up to 30% while maintaining healthy plant development.
DLI (Daily Light Integral) Conversion Chart
Matching your DLI target with your chosen light hours ensures plants receive the right balance of intensity and duration.
| Target DLI | 12 hrs | 14 hrs | 16 hrs | 18 hrs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 mol/m²/day | 350 PPFD | 300 PPFD | 260 PPFD | 230 PPFD |
| 25 mol/m²/day | 590 PPFD | 500 PPFD | 440 PPFD | 390 PPFD |
| 35 mol/m²/day | 830 PPFD | 700 PPFD | 610 PPFD | 540 PPFD |
Tip: It’s often more energy-efficient to extend your light hours slightly rather than pushing higher intensity — especially for smaller home or tent grows.
Troubleshooting Common LED Grow Light Problems
| Plant Symptom | Likely Cause | Quick Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Pale upper leaves | Too much light (bleaching) | Raise or dim your light |
| Stretching | Too little light intensity | Lower your fixture or increase light hours |
| Leaf curling / tacoing | Heat or light stress | Improve airflow and increase light distance |
| Uneven growth | Hotspots or poor light coverage | Adjust fixture angle or add side lighting |
Summary
These quick-reference charts help you maintain the perfect balance between LED grow light intensity, distance, and energy efficiency. Keep them close while setting up or fine-tuning your grow space — small adjustments to lighting height, duration, or uniformity can significantly improve both yield and power savings.
FAQ: Common Questions About LED Grow Lights
Yes, LED grow lights truly work — when you choose a quality model and set it up correctly. Modern full-spectrum LEDs now rival or even outperform traditional HPS and fluorescent systems in both yield and efficiency. Their balanced spectrum and high light efficacy (µmol/J) make them ideal for hobbyists and professional growers alike.
Absolutely. All plants use light in the PAR (Photosynthetically Active Radiation) range — between 400–700 nanometres (nm) — for photosynthesis. The main difference is in light intensity needs. Herbs, leafy greens, and microgreens thrive under moderate PPFD, while fruiting crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and cannabis perform best under higher light intensity for maximum yield and quality.
Not effectively. Regular household bulbs don’t emit enough PAR light or the specific wavelengths plants need. Dedicated LED grow lights are designed to deliver the correct light spectrum, intensity, and coverage that support all stages of plant development.
The best setup uses a full-spectrum white light enhanced with deep red diodes around 660 nm. Blue light supports strong vegetative growth, while red wavelengths trigger flowering and fruiting. Adding small amounts of UV and far-red light can enhance flavours, resin production, and pigmentation — but overdoing it can cause light stress.
Your optimal LED grow light distance depends on both fixture power and growth stage:
Seedlings: 60–75 cm
Vegetative: 45–60 cm
Flowering: 30–45 cm
Start higher and lower gradually as plants adapt. Watch for early signs like leaf bleaching or curling — these often indicate excessive light intensity.
Most indoor plants thrive with 16–18 hours of light daily. Flowering plants such as cannabis follow 18/6 (veg) and 12/12 (flower) photoperiods, while autoflower strains often do best with 18–20 hours of consistent light. Keeping a stable LED grow light schedule helps prevent stress and encourages steady growth.
Yes — but far less than older lighting systems. LEDs emit minimal radiant heat, though their drivers and diodes still warm up during long sessions. Maintain good airflow across the canopy and keep leaf temperatures below 28°C to prevent heat stress and light burn.
Usually, yes. Premium LED grow lights offer better spectrum balance, higher PAR output, and more even coverage. They’re also much more energy-efficient, saving money in the long term. Cheaper lights often exaggerate wattage or PPFD ratings and can lead to uneven growth or reduced yields.
They’re not essential but can boost quality when used carefully. UV light helps increase terpenes, colour, and resin in aromatic plants, while far-red light influences stretching and flowering speed. Introduce these wavelengths in small doses during late vegetative or early flowering stages for the best effect.
High-quality fixtures last about 50,000–60,000 hours before losing noticeable brightness — that’s roughly 8–10 years under regular use. To extend lifespan, keep lenses dust-free, maintain airflow, and avoid running lights at maximum output all the time.
Summary
Modern LED grow lights deliver excellent performance for herbs, salad greens, fruiting plants, and flowering crops. When you balance spectrum, intensity, and photoperiod, you’ll achieve stronger growth, higher yields, and more efficient energy use — all without the heat and cost of traditional grow lights.
Where to Next: Deepen Your LED Grow Light Knowledge
If you’ve made it this far, you already understand how LED grow lights work — and why spectrum, intensity, and efficiency are key to strong, healthy plants. Now it’s time to apply that knowledge and fine-tune your setup. Whether you’re lighting a few herbs on a shelf or running a 4×4 tent packed with fruiting crops, the next step is choosing the best LED grow light for your space and growing goals.
Below you’ll find expert guides designed to take you from theory to practical, real-world growing success.
Next Steps & Recommended Reading
Best LED Grow Lights for a 4×4 Tent (UK)
An in-depth guide for growers seeking full PPFD coverage and maximum yield per square metre.
Best LED Grow Lights for Indoor Gardens
Ideal for smaller setups — perfect for herbs, salad greens, or compact hydroponic systems.
Best LED Grow Lights for Different Types of Plants
Discover which LED light spectrum works best for leafy greens, fruiting vegetables, and flowering plants.
Advanced Tips for Using LED Grow Lights
Level up your grow with techniques on dimming, coverage optimisation, and light spectrum tuning.
Your Next Step
Before purchasing, take a moment to plan your growing space and clarify your goals — are you focused on higher yields, energy efficiency, or long-term sustainability? Each of the guides above helps you choose the right LED grow light setup to meet those objectives.
If you’re looking to expand your indoor gardening knowledge, explore related topics like:
- Indoor vegetable gardening
- Hydroponics vs soil growing
- Energy-efficient LED grow setups
Final Thought
Switching to LED grow lights isn’t just an upgrade — it’s a step toward sustainable, precision-controlled growing. Once you understand how light intensity, distance, and spectrum shape plant development, you can confidently guide your crops from seedling to harvest. Explore the guides above and start optimising your indoor grow light system today.







