Introduction: Why More UK Homes Are Turning to Off-Grid Solar
Energy costs in the UK continue to rise. At the same time, concerns about power cuts, grid reliability, and long-term energy security are becoming harder to ignore. As a result, more homeowners, renters, and small businesses are now exploring off-grid solar systems in the UK as a practical way to take control of their electricity.

Put simply, an off-grid solar system allows you to generate, store, and use your own power without relying on the national grid. Because of this independence, off-grid solar systems are increasingly used for:
- Preparing for power cuts and blackouts
- Powering garden offices, cabins, and workshops
- Supporting off-grid or rural properties
- Moving towards long-term energy independence
Thanks to advances in modern solar technology, off-grid solar systems UK homeowners can install today are far more achievable than they once were. Even in the UK climate, well-planned systems can now provide reliable, everyday power — when they’re designed correctly.
However, one of the biggest challenges with off-grid solar is knowing what size system you actually need. Many guides focus heavily on pre-built solar kits. While these kits can be convenient, they often overlook key UK-specific factors, including:
- Lower winter sunlight levels across much of the UK
- Battery storage requirements for overnight and cloudy-day use
- Real-world appliance choices and day-to-day energy habits

That’s exactly why this guide focuses on off-grid solar systems in the UK, rather than one-size-fits-all kits. Instead, we’ll explain how off-grid solar works under UK conditions, break down the components that matter most, and show you how to size a system that genuinely fits your needs — whether that’s a small emergency backup system or a larger DIY off-grid solar setup.
Along the way, you’ll see practical system examples and modular approaches that can be expanded over time. By the end, you’ll have a clear, grounded understanding of off-grid solar systems, how to plan them properly, and the next steps to building a reliable setup that works in real UK conditions.
If you’re still working out what size setup you actually need, try the solar calculator to estimate panel, battery, and inverter requirements before buying a kit.
Our Free Interactive Off-Grid Solar System Sizing Tool
One of the hardest parts of planning an off-grid solar system in the UK is working out how big the system actually needs to be. Very often, people either underestimate their energy use and end up with an unreliable setup — or, just as commonly, they overestimate, see a large figure, and assume off-grid solar isn’t realistic for them.
On top of that, UK-specific factors make off-grid solar system sizing more challenging than many guides suggest. Short winter days, low sun angles, and a heavier reliance on battery storage mean that generic rules of thumb — especially those based on overseas examples — can be misleading.
That’s exactly why this UK-focused off-grid solar sizing tool exists. Its purpose is simple: to help you plan realistically, understand system scale, and make informed decisions before buying any equipment.
What This Off-Grid Solar Sizing Tool Does
This off-grid solar calculator UK users can rely on is designed for DIY planning and comparison — not for selling products or replacing professional electrical design.
In practical terms, it helps you estimate:
- Daily energy use, based on the appliances you genuinely plan to run
- Battery storage capacity needed for evenings, nights, and low-sun periods
- Solar array size suited to UK conditions, including winter performance
- Inverter size, based on real appliance loads and startup surges
All calculations use conservative UK assumptions, factoring in system losses and realistic run-times. As a result, the figures may appear larger than those from some online solar calculators — and that’s intentional.
What You’ll Need to Enter
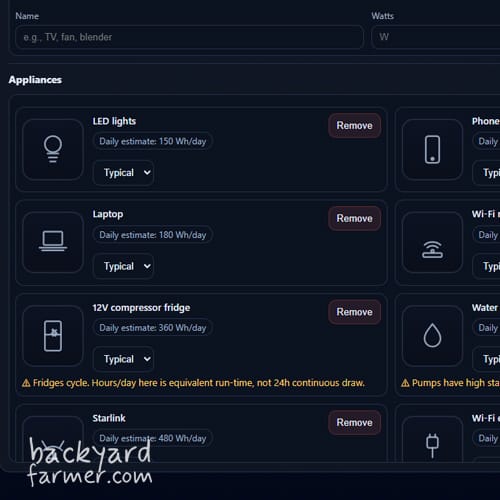
To generate meaningful results, the tool asks for simple, everyday information, such as:
- The appliances you want to power (for example: fridge, lighting, laptop, tools)
- Roughly how long each appliance runs per day
- Whether the system is intended for occasional use, daily off-grid use, or emergency backup
You don’t need technical knowledge or electrical experience. Instead, the calculator works from real-life usage patterns, not abstract formulas.
What Results You’ll See
Once you enter your details, the off-grid solar calculator will show:
- An estimated daily energy requirement (kWh)
- A recommended battery storage size for dependable operation
- A solar panel capacity range appropriate for UK sunlight levels
- A suggested inverter size capable of handling expected loads
Together, these results give you a clear sense of the off-grid solar system size involved — which is often the biggest unknown when planning solar in the UK.
How to Use the Results
The sizing results work best as a planning tool, rather than a pass-or-fail test.
You can use them to:
- Identify which appliances are driving most of your energy use
- Compare summer-only setups with year-round off-grid solar systems
- Decide whether a small solar kit, modular system, or phased build makes sense
- Spot where efficiency improvements or small compromises could reduce system size
If the calculator suggests a very large off-grid solar system, it usually means your energy use is closer to grid-style living — not that the calculator is wrong. In many cases, adjusting appliance choices, refining usage habits, or accepting seasonal limits can significantly reduce what’s required.
A Final Planning Note
This off-grid solar sizing tool is designed to help you understand feasibility and scale before buying any components. While it doesn’t replace professional system design, it does provide something far more useful at the early stages: clarity.
Once you have a clearer idea of system size, it becomes much easier to compare off-grid solar options, plan a realistic budget, and decide whether an off-grid solar system genuinely fits your situation. If you’re new to solar power, it’s worth understanding how panels actually generate electricity before sizing a system — this guide explains how solar panels work in clear, practical terms.
Off-Grid Solar System Sizing Tool (UK)
Use this UK-focused calculator to estimate battery size, solar panel capacity, and inverter requirements based on realistic usage and winter conditions.

Use the Full Solar Sizing System Tool
We’ve moved this calculator into a dedicated full-screen tool for a clearer, more accurate sizing experience. Use it to build your solar sizing system step-by-step, adjust real-world usage, and see exactly what panels, batteries, and inverter capacity you’ll need.
Free to use • No signup required • Designed for UK conditions
What Is an Off-Grid Solar System?
An off-grid solar system is a self-contained power setup that generates and stores electricity without relying on the national grid. In the UK, these systems use solar panels to produce electricity, store that energy in batteries, and then supply power directly to your appliances whenever it’s needed.
Put simply, an off-grid solar system UK homeowners use allows you to make your own electricity and use it on your own terms. Because of this, off-grid solar is especially appealing if you’re aiming for energy independence, reliable backup power, or electricity in places where grid access is limited, unreliable, or not available at all.
How Off-Grid Solar Systems Work
Although the technology can sound complex at first, the way an off-grid solar system works is actually quite straightforward:
- Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into usable electrical energy
- Charge controllers regulate how that energy flows safely into the batteries
- Battery storage holds power for evenings, nights, and low-light conditions
- Inverters convert stored DC electricity into standard AC power for everyday appliances
Together, these components create a steady and reliable power supply. As a result, even when the sun isn’t shining, an off-grid solar system can continue to deliver electricity from stored energy.
Off-Grid vs Grid-Tied and Hybrid Solar Systems
Before deciding whether an off-grid solar system is right for you, it helps to understand how it compares with other common solar setups used in the UK:
- Off-grid solar systems operate independently and rely entirely on battery storage
- Grid-tied solar systems remain connected to the national grid and typically shut down during power cuts
- Hybrid solar systems combine solar panels, batteries, and grid access to provide backup power while still using the grid
Off-grid solar systems offer the highest level of energy independence. However, because there’s no grid to fall back on, they also require more careful planning. As a result, system sizing, battery capacity, and winter performance matter far more than they do with grid-connected solar systems.
Why Batteries Are Essential for Off-Grid Solar in the UK
Batteries are the backbone of any off-grid solar system in the UK. Without battery storage, solar panels can only supply power while the sun is shining.
In UK conditions, batteries play a crucial role because they:
- Store excess solar energy for evening and overnight use
- Provide power during cloudy weather and throughout the winter months
- Help deliver stable, consistent electricity to sensitive electronics and appliances
Modern lithium batteries — particularly LiFePO₄ (lithium iron phosphate) — have made off-grid solar systems far more practical and reliable. Compared to older battery types, they offer longer lifespans, deeper usable capacity, and improved safety.
With these fundamentals covered, the next step is to look more closely at the individual components that make up an off-grid solar system — and how each one affects performance, reliability, and overall cost.
What Makes Up an Off-Grid Solar System?
An off-grid solar system is made up of several core components that work together to generate, store, and deliver electricity reliably. By understanding how each part functions, it becomes much easier to plan an off-grid solar system in the UK that performs well in real conditions — and just as importantly, avoids some of the most common sizing and performance mistakes.
Rather than thinking in terms of fixed, pre-built solar kits, it’s far more useful to understand how individual off-grid solar components contribute to the system as a whole. This system-first approach gives you more flexibility, helps future‑proof your setup, and makes it easier to expand, tweak, or maintain over time.
Solar Panels
Solar panels generate electricity by converting sunlight into usable power. However, when it comes to off-grid solar panels in the UK, panel quality and total wattage matter far more than the sheer number of panels installed.

A few practical points worth keeping in mind:
- Rigid solar panels offer the best efficiency and durability for roofs, ground mounts, and permanent installations
- Portable or flexible panels can suit temporary setups, sheds, campervans, or mobile systems — although they usually produce less power
- Total panel wattage directly affects how much energy your system can generate each day, which becomes especially important during winter
Because UK sunlight levels drop significantly in the colder months, many off-grid solar systems UK users rely on benefit from slightly oversized solar arrays. As a result, this extra capacity helps maintain consistent battery charging when conditions are less than ideal.
Battery Storage
Batteries store the electricity your solar panels generate so it’s available whenever the sun isn’t shining. In any off-grid solar system, battery capacity is one of the most important — and most commonly underestimated — design choices.
In the UK, modern off-grid systems typically use LiFePO₄ (lithium iron phosphate) batteries, as they offer several clear advantages:
- Significantly longer lifespan compared to lead‑acid batteries
- Higher usable capacity without damaging deep discharges
- Improved efficiency and faster charging
- Better safety and long‑term reliability
In practice, battery size determines how long an off-grid solar system can run in the evening, overnight, or through extended periods of low sunlight. When systems feel unreliable, undersized battery storage is often the main cause.
Inverter
The inverter converts the DC electricity stored in your batteries into standard AC power that everyday appliances can use.
When choosing an off-grid inverter, it’s important to consider:
- Continuous power rating, which determines how many appliances can run at the same time
- Surge capacity, which handles short bursts of higher demand from items like fridges, pumps, or power tools
- Pure sine wave output, which is essential for modern electronics and sensitive equipment
For most UK homes, garden offices, and workshops, pure sine wave inverters are the safest and most reliable choice. As a result, they help avoid compatibility issues and protect sensitive devices.
Charge Controllers & System Management
Charge controllers regulate how electricity flows from your solar panels into your batteries. Their role is simple but critical: they prevent overcharging while improving overall system efficiency.
Most modern off-grid solar systems in the UK use MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) charge controllers because they:
- Extract more usable energy from solar panels
- Perform better in low‑light and cold UK conditions
- Improve overall charging efficiency
In some setups — particularly integrated power kits — charge control, inverter functions, and system monitoring are combined into a single unit. As a result, installation is often simpler, and it becomes much easier to monitor performance and spot issues early.
Once you’re clear on the core off-grid solar components, the next step is sizing them correctly for UK conditions. This is where many systems either succeed or struggle, which is why careful planning matters before buying any equipment.
How Big Does an Off-Grid Solar System Need to Be in the UK?
One of the most common mistakes people make with off-grid solar systems in the UK is under-sizing the system. This issue shows up even more often here because sunlight levels vary dramatically throughout the year. A setup that feels perfectly fine in summer can quickly struggle once winter arrives, especially if it hasn’t been planned with UK conditions in mind.

In practical terms, off-grid solar system sizing in the UK comes down to three core factors:
- How much electricity you actually use each day
- How much solar energy your system can realistically generate
- How much energy you need to store for evenings, nights, and low-sun periods
Once these basics are clear, it becomes far easier to avoid unreliable performance, unnecessary frustration, and expensive upgrades further down the line.
Why UK Winter Conditions Matter
When sizing an off-grid solar system UK users can rely on, winter performance matters more than anything else. During autumn and winter, shorter days, lower sun angles, and frequent cloud cover all reduce how much energy solar panels can produce.
As a result:
- Summer solar output can be several times higher than winter output
- Systems sized only around summer use often fall short in colder months
- Battery storage becomes far more important when sunlight is limited
For this reason, planning around winter solar performance, rather than summer peaks, is usually the safest and most realistic approach for off-grid solar in the UK.
Daily Energy Use: Start With Your Appliances
The first step in off-grid solar system sizing is understanding how much electricity you actually use day to day.
This usually involves:
- Listing essential appliances such as lighting, fridges, routers, computers, and tools
- Estimating how many hours each appliance runs per day
- Adding everything together to calculate a realistic daily energy figure in kilowatt-hours (kWh)
Even relatively modest appliances can add up faster than expected. Because of this, realistic estimates are far more useful than optimistic guesses when planning an off-grid solar setup.
Solar Panel Capacity: Generating Enough Power
Your solar panels need to cover daily energy use while also recharging your batteries.
In UK conditions:
- Total panel wattage matters more than the number of individual panels
- Slightly oversizing the solar array improves winter reliability
- Modular panel layouts make future expansion easier and more cost-effective
A larger solar array helps an off-grid solar system recover more quickly after cloudy days, which in turn reduces strain on the batteries.
Battery Capacity: Keeping the Power On
Battery storage determines how long an off-grid solar system can keep running when there is little or no sunlight.
When planning battery capacity, it helps to consider:
- Evening and overnight electricity use
- One or more consecutive low-sun days
- Seasonal changes in solar generation across the UK
In practice, many off-grid solar systems in the UK benefit from one to two days of usable battery storage, depending on how critical the loads are.
Inverter Size: Handling Real-World Loads
The inverter must be powerful enough to handle real-world usage, not just theoretical calculations.
Key factors to consider when choosing an off-grid inverter include:
- Continuous power rating for normal daily operation
- Surge capacity for appliances with startup loads
- Enough headroom to allow for future expansion
If the inverter is undersized, it can quickly become a bottleneck — even when solar panels and batteries are otherwise well matched.
Use an Off-Grid Solar Sizing Tool (UK)
Because all of these variables interact, manual calculations can quickly become confusing. An off-grid solar sizing tool UK users can trust helps simplify the process by estimating realistic system requirements based on actual usage and UK conditions.
A reliable solar sizing calculator will typically estimate:
- A suitable solar array size
- Battery capacity needed for dependable performance
- An appropriate inverter size
Using a calculator before buying any equipment gives you a much clearer idea of what’s realistic. More importantly, it helps ensure your off-grid solar system performs well year-round and avoids costly mistakes.
Once you have a clear idea of system size, the next step is understanding how different off-grid solar system types are commonly used in the UK — and which approach best fits your needs.
Common Off-Grid Solar System Types (UK Examples)
Once you’ve used the sizing tool and have a clearer idea of your daily energy use, battery requirements, and solar capacity, the next step is understanding how off-grid solar systems are commonly set up in the UK.
In reality, most DIY off-grid solar systems in the UK fall into a handful of practical categories. These aren’t fixed templates or strict rules. Instead, they act as a useful way to sense-check your sizing results and see which type of off-grid solar setup is most likely to suit your needs.
Small Emergency Backup Off-Grid Solar Systems
Best for:
- Power cuts and short outages
- Flats, small homes, sheds, and outbuildings
- Keeping essential devices running
Typical loads:
- Lighting
- Phone and laptop charging
- Wi‑Fi router
- Efficient fridge or freezer

Key characteristics:
- Modest battery storage designed mainly for overnight use
- A solar array sized for recovery after outages, rather than full daily supply
- An inverter chosen for essential loads, instead of whole‑home power
These small off-grid solar systems focus on resilience rather than replacement. While they won’t replicate grid-style living, they can keep critical devices running during outages and reduce reliance on generators.
If your off-grid solar calculator results land in this range, it often means your energy use is already efficient, selective, and well suited to backup-style off-grid power.
Medium DIY Off-Grid Solar Systems (Cabins & Garden Offices)
Best for:
- Garden offices and workshops
- Cabins and weekend retreats
- Daily work setups with controlled energy use
Typical loads:
- Computers and monitors
- Lighting
- Fridge
- Small tools and equipment

Key characteristics:
- Larger battery capacity to support regular daily use
- A solar array sized for steady, consistent recharging
- An inverter with enough headroom to handle startup surges
This is the most common category for DIY off-grid solar systems in the UK. As a result, it strikes a practical balance between reliability and complexity and is often where people first experience genuine energy independence from the grid.
Sizing results in this range usually point to intentional off-grid living, where appliances are chosen to suit solar power rather than forcing solar to behave like mains electricity.
Larger Home Backup & Off-Grid Solar Systems
Best for:
- Rural homes
- Long-duration power outages
- High-resilience or near off-grid living
Typical loads:
- Fridge and freezer
- Lighting throughout the home
- Communications and office equipment
- Selected kitchen or utility appliances

Key characteristics:
- Significant battery storage to cover extended low‑sun periods
- Larger or deliberately oversized solar arrays for winter reliability
- Inverters capable of running multiple appliances at the same time
These larger off-grid solar systems in the UK require the most planning and usually involve compromises, such as load management or seasonal adjustments. If your calculator suggests a system of this size, it doesn’t mean off-grid solar isn’t viable — instead, it highlights grid‑level energy expectations.
In many cases, reviewing appliance choices, improving efficiency, or accepting limits on high‑draw devices can significantly reduce both system size and overall cost.
How to Use These Off-Grid Solar System Categories
Treat these off-grid solar system types as a sense check, not a rulebook.
They help you:
- Compare your off-grid solar sizing results with real‑world UK setups
- Decide whether a simple solar kit or a modular off-grid system makes more sense
- Understand why winter‑ready off-grid solar systems are often larger than expected
In the next section, we’ll look at how these system types translate into practical, modular off-grid solar systems, and how to choose components that can be expanded over time.
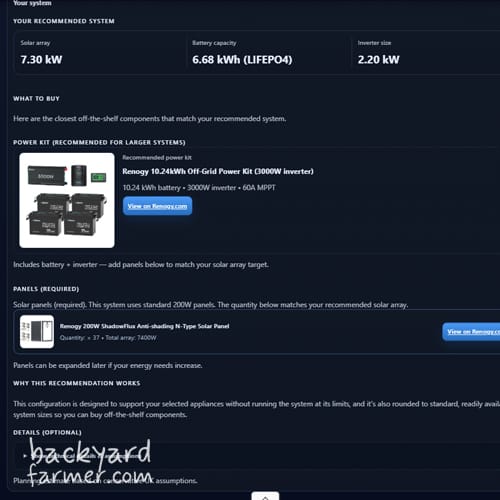
Recommended Renogy Off-Grid Solar Systems (UK)
Once you’ve got a clearer idea of your system size and which off-grid category you fall into, the next step is choosing components that are reliable, modular, and realistic for UK conditions. At this stage, many people look for proven brands that support DIY builds without forcing them into inflexible kits.
Rather than relying on fixed, one-size-fits-all solutions, many UK DIYers prefer modular off-grid solar systems that can grow over time. This approach works particularly well if your energy needs change, or if you’d rather start modestly and expand later. Renogy off-grid solar systems in the UK suit this style because their batteries, inverters, and solar panels are designed to scale together — without locking you into a rigid setup.
The examples below aren’t strict designs or shopping lists. Instead, they’re practical reference systems that show how typical off-grid solar sizing results translate into real-world builds using Renogy components.
Renogy Off-Grid Solar System for Small Emergency Backup
Best for:
- Power cuts and short outages
- Flats, small homes, sheds, and outbuildings
- Keeping essential devices running
Typical system characteristics:
- Modest battery storage aimed mainly at overnight use
- A solar array sized for recovery after outages, rather than full daily supply
- An inverter chosen for essential loads, instead of whole-home power

How this looks in practice:
- A compact LiFePO₄ battery setup to cover evening and overnight use
- A modest solar panel array that recharges batteries during daylight hours
- A pure sine wave inverter with enough surge capacity for fridges and electronics
This type of Renogy off-grid solar system focuses on resilience rather than capacity. While it won’t replace grid living, it can provide genuine peace of mind during power cuts without adding unnecessary cost or complexity.
Renogy Off-Grid Solar System for Cabins and Garden Offices
Best for:
- Garden offices and workshops
- Cabins and weekend retreats
- Daily work setups with controlled energy use
Typical system characteristics:
- Larger battery storage to support regular daily operation
- A solar array sized for steady, consistent recharging
- An inverter with enough headroom to handle startup surges

How this looks in practice:
- A 24V battery configuration for improved efficiency
- A modular Renogy solar array that can be expanded as needs change
- An inverter sized to comfortably handle office equipment and light tools
This is the most common category for DIY off-grid solar systems in the UK. As a result, it strikes a practical balance between reliability and complexity and is often where people first experience genuine energy independence from the grid.
Renogy Power Kits for Larger Home Backup Systems
Best for:
- Rural homes
- Long-duration power outages
- High-resilience or near off-grid living
Typical system characteristics:
- Significant battery storage to bridge extended low-sun periods
- Larger or deliberately oversized solar arrays for winter reliability
- Integrated inverter, charge control, and system monitoring
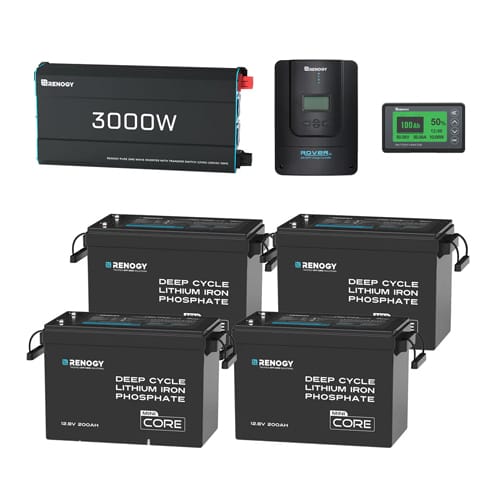

How this looks in practice:
- A Renogy power kit combining inverter, charge control, and monitoring
- Expandable battery modules that can be added over time
- A solar array designed around winter performance, rather than summer peaks
Renogy power kits reduce wiring complexity and simplify installation. At the same time, they still allow modular expansion — an important factor if you want to build capacity gradually instead of committing to everything upfront.
Choosing the Right Renogy Off-Grid Solar System
If you’re unsure which Renogy off-grid system makes the most sense, use your sizing results as a starting point:
- Smaller results usually point towards an emergency backup solar system
- Mid-range results often suit cabin or garden office off-grid setups
- Larger results tend to indicate home backup or near off-grid living
It’s also worth remembering that off-grid solar systems in the UK don’t have to be built all at once. Many successful Renogy setups start small and grow steadily as usage patterns become clearer and confidence builds.
In the next section, we’ll compare off-grid solar systems and pre-built solar kits, and explain when each approach makes sense for UK users.
Off-Grid Solar Systems vs Pre-Built Solar Kits (UK)
When you start researching off-grid solar systems in the UK, you’ll quickly come across pre-built solar kits alongside fully modular off-grid setups. At a glance, both options can work. However, in practice, they suit very different needs, budgets, and expectations — especially under real UK conditions.
Understanding the difference early on helps you avoid buying a solar kit that looks convenient on paper, but then falls short once it’s actually in use.
When Pre-Built Off-Grid Solar Kits Make Sense
Pre-built off-grid solar kits are usually sold as bundled packages. Typically, they include solar panels, a battery (or batteries), a charge controller, and sometimes an inverter.
In the UK, these kits can be a sensible option if:
- Your energy use is very low and predictable
- The system is intended for occasional or seasonal use
- You want a simple entry point with fewer decisions to make
- Future expansion isn’t important
For example, smaller off-grid solar kits often work well for:
- Sheds or workshops used infrequently
- Summer-only cabins or holiday lets
- Basic emergency charging for phones, lights, and small devices
In these cases, the convenience of a ready-made kit can outweigh its limitations.
The Limitations of Pre-Built Solar Kits in the UK
While pre-built solar kits are often marketed as complete off-grid solutions, they can feel restrictive in real-world UK conditions.
Common limitations include:
- Undersized battery storage that struggles during winter or extended cloudy periods
- Limited inverter capacity that restricts which appliances you can realistically run
- Little or no room to expand as your energy needs change
- Solar arrays sized for ideal conditions, rather than UK winter reality
Because many off-grid solar kits are designed for broad, international markets, they don’t always reflect the lower sunlight levels and heavier reliance on battery storage typical in the UK.
Why Modular Off-Grid Solar Systems Are Often a Better Fit
A modular off-grid solar system is built from individual components chosen around your actual energy use, rather than an assumed average.
This system-first approach allows you to:
- Size batteries realistically for overnight and winter use
- Choose an inverter that matches real appliance loads
- Add solar panels or battery capacity later as your setup evolves
- Build the system in stages, instead of paying for everything upfront
For many UK users — particularly those planning year-round off-grid solar — modular systems offer better reliability, flexibility, and long-term value than fixed kits.
Using an Off-Grid Solar Sizing Tool to Decide
Your off-grid solar sizing tool results provide a helpful reference when deciding between a solar kit and a modular system:
- Very small system requirements may suit a simple pre-built off-grid solar kit
- Mid to large system requirements usually point towards a modular off-grid solar system
- Larger results often highlight grid-style energy expectations that most kits can’t realistically support
If the calculator suggests a larger system than expected, it doesn’t mean off-grid solar isn’t viable. More often, it shows that a kit-based approach may be too inflexible for how you want to use power in the UK.
A Balanced Off-Grid Solar Approach
In reality, many people take a mixed route. Some start with a small off-grid solar kit and later transition to a modular system, while others build modular setups from day one and expand gradually.
There’s no single right answer. However, understanding the trade-offs helps you make a decision based on reliability, flexibility, and realism, rather than marketing claims.
In the next section, we’ll look at off-grid solar installation options, including what most DIY users can safely handle themselves and when professional help makes sense in the UK.
Installation Options: DIY or Professional? (UK)

One of the big advantages of modern off-grid solar systems in the UK is that many setups are now well within reach of confident DIY users. At the same time, there are situations where bringing in a professional is the safest — and often the most sensible — option.
Understanding where that line sits helps you plan your off-grid solar installation with confidence, while avoiding shortcuts or unnecessary risks.
What Many DIY Users Can Do Safely
For small to medium off-grid solar systems — especially those used for cabins, garden offices, sheds, and emergency backup — a large part of the installation is manageable for experienced DIYers.
This typically includes:
- Mounting solar panels on sheds, ground frames, or suitable roofs
- Assembling battery storage according to manufacturer instructions
- Connecting charge controllers and basic system monitoring equipment
- Setting up off-grid inverters for standalone operation
Fortunately, modern off-grid solar components are clearly labelled, modular, and designed to reduce wiring complexity. As long as you take your time, follow guidance carefully, and double‑check every connection, DIY off-grid solar installation in the UK can be both safe and rewarding.
When Professional Help Makes Sense
However, there are situations where involving a qualified electrician or off-grid solar installer is strongly recommended — and often well worth the cost.
This usually applies to:
- Systems supplying power to fixed household circuits
- Installations using high-capacity inverters or large battery banks
- Any setup connected to an existing consumer unit
- Situations where building regulations or insurance requirements apply
In the UK, electrical work that feeds into permanent household wiring may fall under Part P of the Building Regulations. In these cases, a professional can ensure your off-grid solar system installation is compliant and provide any certification you may need.
A Hybrid Off-Grid Solar Installation Approach
In practice, many UK users choose a hybrid approach. They handle the physical installation and system assembly themselves and then bring in a professional for final checks or any grid-adjacent connections.
This approach can:
- Keep overall installation costs down
- Help you understand how your off-grid solar system actually works
- Provide peace of mind around safety, compliance, and insurance
For many DIY‑minded users, this strikes the right balance between independence and responsibility when installing an off-grid solar system.
Safety First, Always
No matter who installs the system, safety should always come first.
Key points to keep in mind during any off-grid solar installation include:
- Correct fusing and appropriately sized cables
- Secure mounting for solar panels and battery storage
- Adequate ventilation, particularly for batteries
- Clear labelling of all off-grid circuits
A cautious, well-planned installation doesn’t just protect your equipment. It also ensures your off-grid solar system in the UK remains safe, reliable, and easy to live with over the long term.
In the next section, we’ll look at off-grid solar system maintenance and long-term reliability, including how to keep your setup performing well year after year.
Maintenance & Long-Term Reliability (Off-Grid Solar Systems UK)

One of the quieter advantages of off-grid solar systems in the UK is that they’re generally low maintenance. However, like any energy system you rely on day to day, a small amount of regular care makes a noticeable difference — particularly in real UK weather conditions.
When an off-grid solar system is properly maintained, it becomes more predictable, easier to live with, and far less likely to let you down when you actually need it.
Solar Panel Maintenance and Cleaning
Solar panels don’t have moving parts, so there’s very little to go wrong. Even so, basic solar panel maintenance helps keep output consistent over the long term.
In the UK, this usually involves:
- Checking panels a few times a year for dirt, moss, bird droppings, or fallen debris
- Cleaning panels if output drops noticeably, especially after winter
- Inspecting mounting hardware for loose fixings following high winds or storms
While rainfall often keeps panels reasonably clean, shaded locations and low winter sun angles can reduce performance if dirt or moss builds up over time.
Battery Maintenance and Health Monitoring
Batteries are the heart of any off-grid solar system, so looking after them is time well spent.
Good solar battery maintenance usually comes down to a few simple habits:
- Avoiding repeated deep discharges beyond manufacturer recommendations
- Installing batteries in a dry, well-ventilated location
- Monitoring state of charge and overall usage patterns
Fortunately, most modern lithium batteries for off-grid solar systems include built-in monitoring or Bluetooth apps. As a result, it’s much easier to spot issues early and adjust how you use power if needed.
Inverter and Electrical System Checks
Although inverters are largely hands-off, it’s still worth checking them — and the surrounding electrics — from time to time.
Routine checks usually include:
- Inspecting cables and terminals for signs of heat, wear, or corrosion
- Making sure ventilation openings remain clear and unobstructed
- Paying attention to warning lights, alerts, or unusual noises
If your off-grid solar system includes monitoring software or firmware updates, keeping these up to date can improve stability, efficiency, and long-term reliability.
Planning for Future Expansion
One of the biggest advantages of modular off-grid solar systems is that they can expand as your energy needs change.
To make future upgrades easier:
- Leave physical space for additional battery storage or extra inverters
- Stick to standard solar panel sizes that are easy to match later
- Keep notes on cable sizes, fuse ratings, and overall system layout
A small amount of forward planning now can save significant time, cost, and frustration later on.
Reliability in Real UK Conditions
In the UK, off-grid solar systems are most reliable when they’re planned around winter performance, rather than summer peaks.
In practical terms, this usually means:
- Slightly oversized solar arrays to compensate for lower winter sunlight
- Sufficient battery storage to cover extended low-sun periods
- Sensible load management during prolonged cloudy weather
With realistic expectations, good system design, and occasional checks, a well-built off-grid solar system can deliver dependable power for many years.
In the next section, we’ll answer some of the most common questions about off-grid solar systems in the UK.
FAQs About Off-Grid Solar Systems UK
Below are some of the most common questions people ask when planning an off-grid solar system in the UK. These answers are based on real-world UK conditions and practical, DIY-focused setups — not idealised marketing examples.
Yes, off-grid solar systems are legal in the UK. You’re allowed to generate and use your own electricity, provided the system is installed safely.
However, if your off-grid solar setup connects to fixed household wiring or a consumer unit, parts of the work may fall under Building Regulations (Part P). In those cases, the installation should be carried out — or at least signed off — by a qualified electrician.
By contrast, standalone off-grid solar systems that power dedicated sockets, cabins, sheds, or fully off-grid buildings usually involve far fewer regulatory requirements.
Yes, an off-grid solar system can power a whole house in the UK, but it requires careful planning and realistic expectations.
In most cases, whole-house off-grid solar systems need:
Substantial battery storage for overnight and winter use
Solar arrays sized for UK winter conditions, not summer peaks
Sensible management of high-draw appliances
Because of this, many UK users adopt a selective-load approach. Rather than trying to replicate full grid living year-round, they power essentials such as lighting, refrigeration, and communications, while managing heavier loads more deliberately.
The cost of an off-grid solar system in the UK varies widely depending on system size, daily energy use, and whether installation is DIY or professionally handled.
As a general guide:
– Small emergency backup systems: lower four-figure range
– Medium cabin or garden office systems: mid four-figure range
– Larger home backup systems: higher four figures or more
Using an off-grid solar sizing tool early in the planning stage helps align expectations with budget and reduces the risk of under- or over-spending.
Yes, off-grid solar can work well in the UK climate, provided systems are designed around winter performance, not summer output.
Off-grid solar tends to be most worthwhile for:
– Emergency backup and energy resilience
– Cabins, garden offices, and rural properties
– People who are happy to manage energy use intentionally
Most issues arise when systems are undersized or based on overseas examples that don’t reflect UK sunlight levels and seasonal variation.
Yes — and for many people, this is the most practical approach.
Modular off-grid solar systems allow you to:
– Add extra solar panels as space or budget allows
– Increase battery capacity over time
– Upgrade inverters if your energy demands change
Starting with a well-sized core system and expanding gradually is often more realistic than trying to build everything at once.
When an off-grid solar calculator suggests a larger-than-expected system, it usually points to one of two things:
– High daily energy use from appliances such as heaters, kettles, or electric cooking
– Expectations closer to grid-style living, rather than selective off-grid use
This doesn’t mean off-grid solar isn’t viable. More often, it highlights where energy use can be adjusted, appliances swapped, or seasonal limits accepted to reduce overall system size.
These FAQs cover the most common questions about off-grid solar systems in the UK. In the final section, we’ll bring everything together and help you decide whether off-grid solar is the right fit for your situation.
Conclusion: Is an Off-Grid Solar System Right for You?
An off-grid solar system in the UK can be a genuinely effective way to take control of your energy use — but only when it’s planned realistically. In practice, success usually comes down to understanding how much electricity you actually use, designing around UK winter conditions, and choosing an off-grid solar system that fits how you live, rather than trying to force solar to behave like the national grid.
For most people, off-grid solar isn’t about cutting the cord overnight. Instead, it’s often about:

- Building resilience against power cuts and outages
- Powering cabins, garden offices, and rural or off-grid properties
- Reducing day-to-day reliance on grid electricity
- Gaining a clearer understanding of household energy use
In reality, the most reliable off-grid solar systems UK users rely on are rarely the smallest or cheapest on paper. Instead, they’re the systems that are sized conservatively, built with quality components, and designed to expand gradually as energy needs change.
If you’re considering an off-grid solar system, the most important first step isn’t choosing solar panels or batteries — it’s understanding off-grid solar system sizing. A UK-focused off-grid solar sizing tool helps show what’s realistic, where compromises might be needed, and whether a small starter system or a larger modular off-grid solar setup makes the most sense for your situation.
Ultimately, off-grid solar works best when expectations are clear and decisions are well informed. With careful planning, realistic assumptions, and a willingness to adapt energy use to seasonal changes, an off-grid solar system can deliver dependable power and long-term peace of mind in real UK conditions.
If you’re ready to explore your options, start by reviewing your sizing results, comparing different off-grid solar system approaches, and building a setup that fits your needs — not marketing promises.
If you want to go deeper into system components, installation tips, and real-world solar use, Renogy’s blog is a useful resource for expanding your understanding beyond basic sizing.







